Making sustainable products the norm
The economic model we currently follow, known as ‘take-make-replace,’ has negative consequences such as resource depletion, environmental pollution, biodiversity loss, and climate change. The “take-make-use-dispose” pattern does not provide producers and their designers with incentives to make their products more circular. Additionally, it fosters Europe’s reliance on external resources.
This is why, the EU is transitioning towards a circular economy model that based on the production of sustainable goods. On 30 March 2022, the EU Commission launched the proposal for the Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation – the cornerstone of its’ strategy to make sustainable products the norm.
The new rules build on the existing Ecodesign Directive, which sets ecodesign requirements at EU level for energy-related products. They cover almost all products on the EU market for maximum environmental and economic benefit.
Circular Economy knowledge
Whereas a common believe is, that circular economy only covers waste, the opposite is true.... (flip)
Design is crucial for circularity
Circular approaches cover all stages of the lifecycle of a product. The design stage determines up to 80% of a product's lifecycle environmental impact.
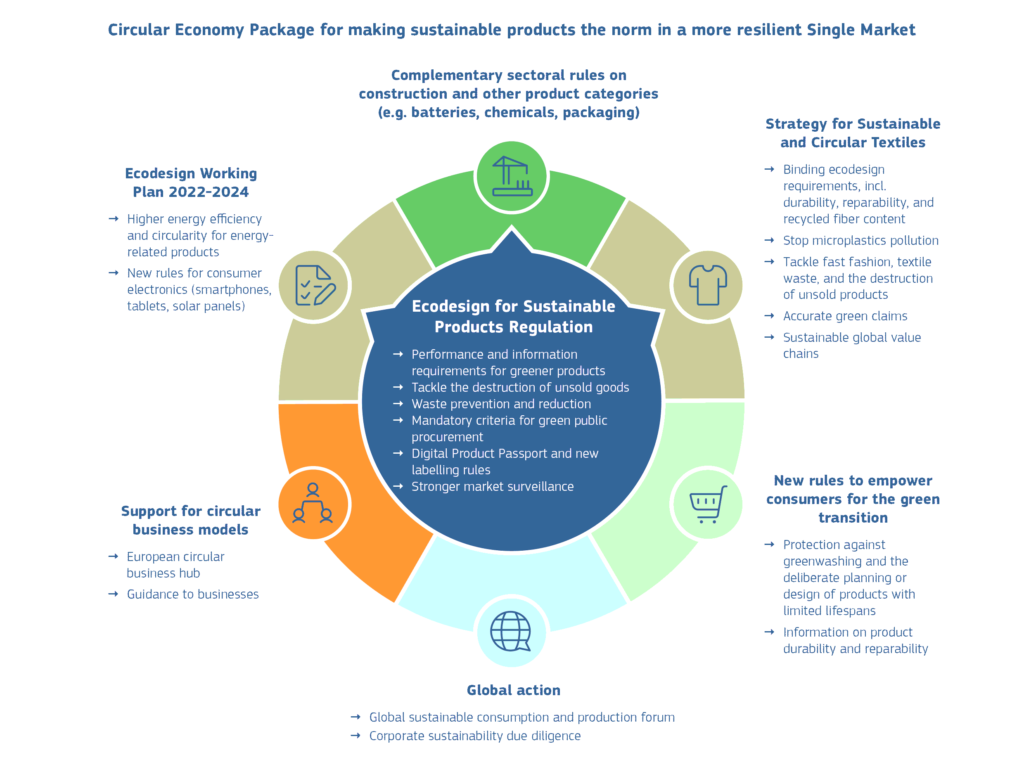
WHAT ARE THE OBJECTIVES OF THE SUSTAINABLE PRODUCT REGULATION?

establishing a framework to set common sustainability requirements for a
broad range of products to be put on the EU market, be they manufactured in or
imported to the EU.
improving product performance and extending product lifetime;
supporting informed decision making, improving product information; and
providing financial savings (due to longer life and less energy use).
- reducing costs for materials, energy and waste management, re-designing
business models, production processes and products, and participating in a wellfunctioning
market for secondary raw materials;
improving resilience of businesses;
providing incentives to innovate and invest in circular business models and the
products of tomorrow;
enhancing transparency across the supply chain, and thus
providing opportunities to improve reputation.
Steps towards sustainable products:
- Enhance the ecological design requirements to ensure that products are more environmentally friendly, circular, and energy efficient.
- Enhance the availability of environmental sustainability information for consumers and participants in the supply chain by introducing Digital Product Passports.
- Prevent the disposal or destruction of unsold consumer products.
- Encourage the adoption of sustainable business models.
- Establish mandatory criteria for green public procurement.
Sustainable Products benefit ALL
Addressing the environmental impact of products throughout their life cycle, will lead to more sustainable, circular and more resource efficient products. More sustainable electronics, furniture, textiles and other products will contribute to the resilience of the EU and global economy.
BENEFITS FOR BUSINESSES
• Reduce administrative and compliance costs • Ensure level playing field • Create competitive edge globally

BENEFITS FOR THE ECONOMY
• Decouple economic growth from energy and resource use • Increase resilience to external shocks, reduce dependencies • Strengthen market for recycled materials

BENEFITS FOR THE ENVIRONMENT
• Help reduce impacts on climate, environment and biodiversity • Remove the most polluting products from the EU market • Reduce negative impacts along product value chains

BENEFITS FOR CONSUMERS
• Extend lifetime of products • Save energy, resources and costs • More information to make sustainable choices
More information :



